Located on the ecological corridor that crosses the Gers between the Landes forest in the West and the Garonne Valley in the East, the Coteaux Gascons area is an essential corridor allowing species to move around, thus constituting a biological area of European importance between Spain and the rest of France and Europe.
The sector includes 260,000 ha, covering 163 municipalities among the most pastoral of Astarac and Armagnac with 25 pre-identified “LIFE biodiversity reservoirs”.
6 Natura 2000 sites are concerned in their entirety or in part:
FR7200806 Hydrographic network of the Midou and Ludon
FR7300893 Lizet and Osse hillsides towards Montesquiou
FR7300897 Valley and hillsides of the Lauze

Meadows, grasslands, moors… Agro-pastoral open spaces are real reservoirs of biodiversity, sheltering a rich fauna and flora and are capable of providing numerous ecosystem services. These environments are therefore a real environmental, but also societal and economic challenge.
Today, these environments are increasingly threatened. Almost half of the species (40%) decline when grasslands are removed. Between 1988 and 2010, a disappearance of 50% of the grasslands has been observed in the department of Gers, while they are real carbon sinks.
These dangers have a direct impact on livestock with 770 fewer farmers between 2010 and 2019.
The following habitats can be found on the territory:
The following 7 species (Annex II of the Habitats, Fauna, Flora Directive) are linked to the BAMs for all or part of their life cycle.
Birds: Black kite (Milvus migrans), Saint Martin’s harrier (Circus cyaneus), Short-toed Eagle (Circaetus gallicus), European nightjar (Caprimulgus europaeux), Lulu lark (Lullula arborea), Red-backed shrike (Lanius collurio)…
Among the vegetation : Bug orchid (Anacamptis coriophora), Bristly broom (Echinospartum horridum) Vanilla orchid (Orchis coriophora subsp. fragans) …
Ecosystem services represent the benefits offered to human societies by ecosystems. There are four categories of services:
APOEs provide us with different ecosystem services: CO2 storage, water management during floods, soil erosion control, pollination, characteristic landscape ….
3 words to understand everything
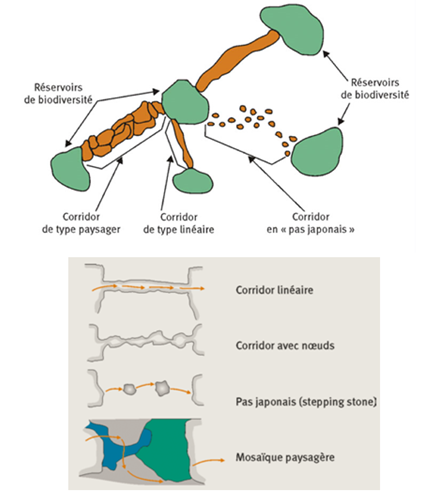
Biodiversity reservoirs: areas rich in biodiversity where individuals can carry out their entire life cycle (reproduction, feeding, shelter…)
+
Ecological corridors: movement routes used by fauna and flora that link biodiversity reservoirs
=
Ecological continuities: associations of biodiversity reservoirs and ecological corridors. Ecological continuities are considered to be functional when they are made up of environments with diversified natural characteristics that are favorable to their movement and when they are not very fragmented.